CRC
这俩计算好像不太一样,好像方案1更简单
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
package d2d.common
import chisel3._
import chisel3.util._
/**
* CRC Generation
* **this is because result is inverted,so 0=15 1=14 ...**
* Polynomial x16 + x12 + x5 + x0 (Visual represenation below) 1_0001_0000_0010_0001
*
* +------------------------+---------------------------------+
* | | |
* | v v
* -->x--+->15 14 13 12 11--->x--->10 9 8 7 6 5 4--->x---->3 2 1 0
* ^ |
* | |
* +-------------------------------------------------------------------------------+
*/
/**
* CRC Generation
* **below show u wher to place xor gate**
* Polynomial x16 + x12 + x5 + x0 (Visual represenation below) * 1_0001_0000_0010_0001 *
*
* +-------------------+---------------------------------+
* | | |
* | v v
* in(MSB)-->x--+->0 1 2 3 4--->x--->5 6 7 8 9 10 11--->x---->12 13 14 15
* ^ |
* | |
* +-----------------------------------------------------------------------------+
* x means xor gate
*/
class crcGen(val width: Int, val dummyImport: Boolean = false) extends Module{
val io = IO(new Bundle{
val in = Input (UInt(width.W))
val out= Output(UInt(16.W))
})
val numBytes = scala.math.ceil(width / 8.0).toInt
val totalBits = numBytes * 8
val paddedData = Wire(UInt(totalBits.W))
val extraZeros = Wire(UInt((totalBits-width).W))
extraZeros := 0.U
paddedData := Cat(extraZeros, io.in)
// This is going to be out XOR variables for each entry, 16 total
// What we plan to do is add in the XORing for each bit as a "shift" operation
var crcMap = scala.collection.mutable.Map[Int, scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer[Int]]()
for (i <- 0 until 16){
crcMap(i) = scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer[Int]()
// -1 will represent the initial SEED for this CRC, in this case the seed is 0xFFFF
// so when a -1 is seen in the map it's viewed as a 1'b1
crcMap(i) += -1
}
for(chunk16 <- 0 until numBytes){ //could probably just be a totalBits?
for (chunkbit <- 0 until 8){
val newCrcIn : scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer[Int] = crcMap(0).clone += ((chunk16*8)+chunkbit) // crcMap(0) is going to xor with in((chunk16*8)+chunkbit)
// means i of 16 in the result is comnputed by xoring all components in crcMap(i)
for (i <- 0 until 16){
i match {
case 3 => crcMap(i) = newCrcIn ++ crcMap(i+1)
case 10 => crcMap(i) = newCrcIn ++ crcMap(i+1)
case 15 => crcMap(i) = newCrcIn
case _ => crcMap(i) = crcMap(i+1)
}
// Remove all of the XOR variables that have more than one instance, since something XOR'ed with itself is 0
crcMap(i) = crcMap(i).groupBy(x=>x).filter(_._2.lengthCompare(1) == 0).keySet.to(scala.collection.mutable.ListBuffer)
}
}
}
val crcCalc = Wire(Vec(16, Bool()))
// This is where we will create the XORing for each crc output bit
val xorList = Seq.tabulate(16){i => Wire(Vec(crcMap(i).size, Bool()))}
for(i <- 0 until 16){
var bindex = 0
crcMap(i).foreach{ j =>
if(j != -1) {
xorList(i)(bindex) := paddedData(j).asBool //io.in(j).asBool
} else {
xorList(i)(bindex) := true.B
}
bindex += 1
}
crcCalc(i) := xorList(i).reduce(_^_)
}
io.out := crcCalc.asUInt
}
object crcGen{
def apply[T <: Data](in: T): UInt = {
val crcgen = Module(new crcGen(in.getWidth))
crcgen.io.in := in
crcgen.io.out
}
}
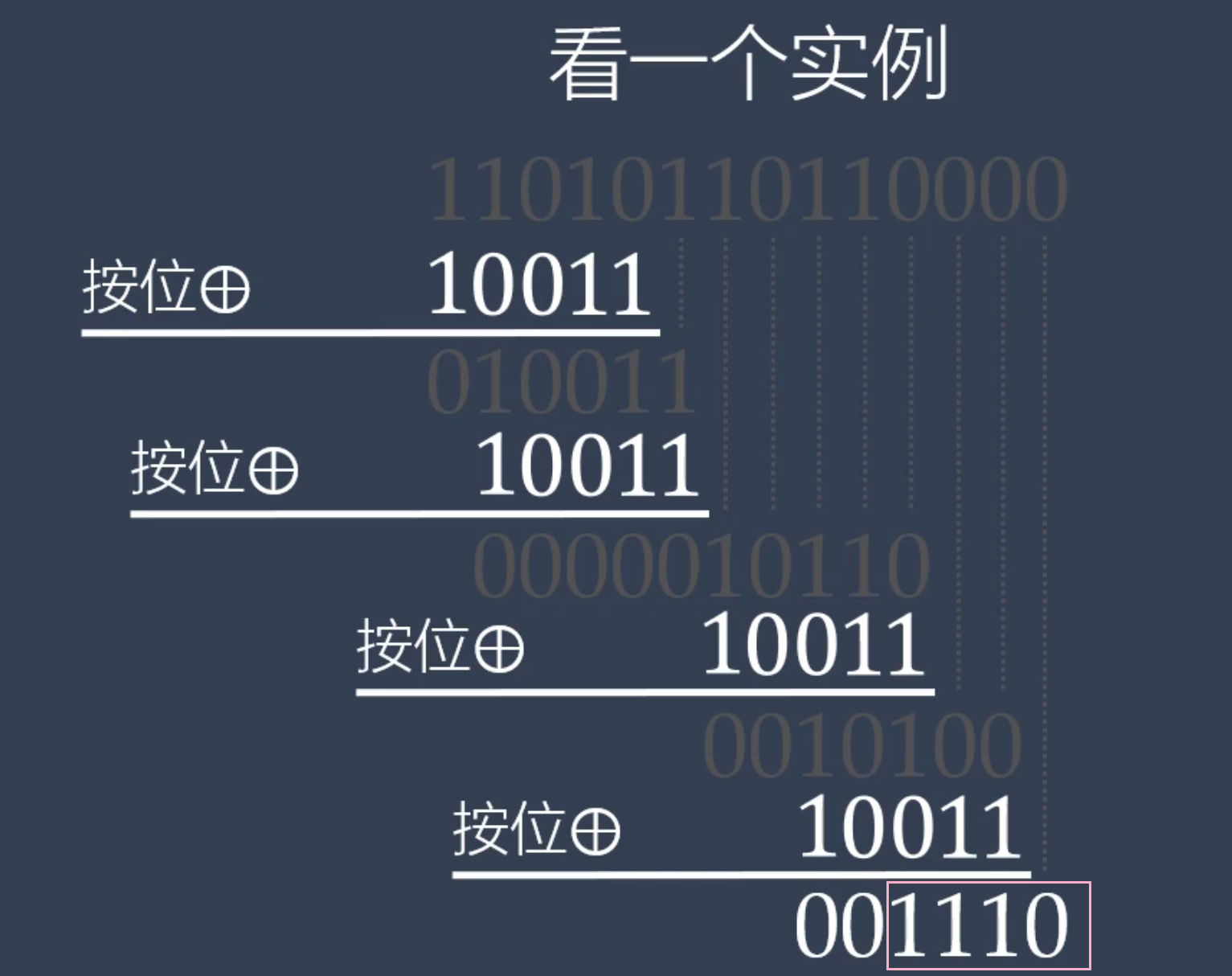
这个是方案2 step1:根据多项式来获得CRC除数:
$x^{6}+x^{4}+x^2+x+x^0$的CRC除数为:101_0111step2:将你要校验的数据串末尾添加6个0(最大项系数)
数据串1101011011_000000
step3:循环处理
最后得到的就是CRC校验和(长度为CRC除数-1)
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.